A-B-C Blog
What is an Orthopedic Implant and How Does It Work?
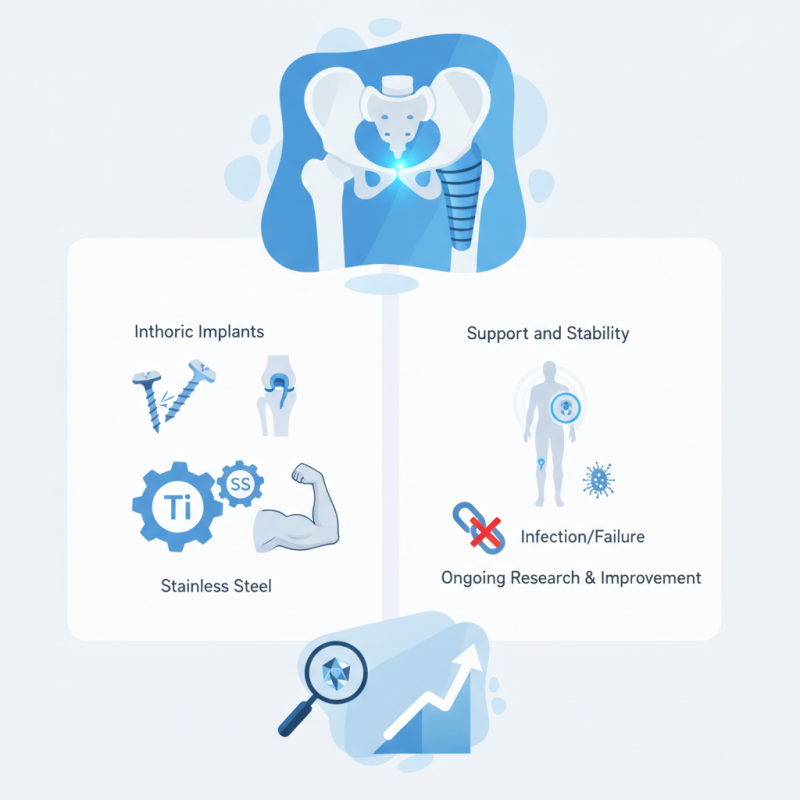
orthopedic implants have transformed modern medicine, offering solutions for various musculoskeletal issues. These medical devices help support, stabilize, and replace damaged bones or joints. From hip replacements to screws and plates, orthopedic implants play a critical role in many surgeries. They come in various shapes and sizes, tailored to individual patient needs.
Understanding how an orthopedic implant works requires diving into its materials and functions. Most implants are made from metals like titanium or stainless steel. These materials provide the strength needed for healing and mobility. As patients recover, the implant supports the injured area while allowing for natural movement.
However, the use of orthopedic implants is not without challenges. Some patients may experience complications, like infection or implant failure. These issues underline the need for careful selection and placement of each device. Ongoing research aims to improve implant design and minimize risks. As we explore this fascinating topic, we will uncover both the benefits and the concerns associated with orthopedic implants.
Definition and Classification of Orthopedic Implants
Orthopedic implants are medical devices used to stabilize or replace damaged bones and joints. They come in various types, each designed for specific conditions. Common classifications include plates, screws, pins, and joint replacement systems. According to a market report, the orthopedic implant market is projected to reach USD 70 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the increasing demand for surgical interventions.
Implants are used in surgical procedures to restore mobility and alleviate pain. They facilitate healing and improve the quality of life. However, challenges persist in ensuring compatibility with human tissue. In some cases, the body may not accept the implant, leading to complications. Statistics indicate that around 5% of patients experience implant-related issues.
The classification of orthopedic implants often depends on materials and functions. For example, titanium is widely used for its strength and biocompatibility. Unfortunately, the high cost can limit access for many patients. Innovations in manufacturing techniques could resolve some of these hurdles. Nonetheless, there remains a need for improved patient education regarding the risks and benefits of implants.
Material Composition and Biocompatibility of Orthopedic Implants
Orthopedic implants play a crucial role in modern medicine. They are used to replace or support damaged bones and joints. The material composition of these implants significantly affects their performance. Common materials include titanium, stainless steel, and polymers. Each material offers unique benefits, such as strength, weight, and biocompatibility.
Biocompatibility is vital for an implant's success. It refers to how well the body accepts the implant without causing an adverse reaction. Titanium is widely used due to its excellent biocompatibility. However, not all patients may tolerate it well. Some individuals experience allergic reactions or prolonged inflammation. It's essential to consider these factors during surgery.
*Tip: Always discuss with your surgeon about any known allergies or past reactions to materials used in surgeries.*
Another aspect is the surface finish of the implant. A rough finish can promote bone growth. However, if it is too rough, it may irritate surrounding tissues. Balancing these factors is not easy and requires ongoing research.
*Tip: Ask your medical team about the materials used in your specific implant and their potential side effects.*
Mechanisms of Action: How Orthopedic Implants Facilitate Healing
Orthopedic implants serve as critical tools in facilitating healing after injuries or surgeries. They help stabilize bones or joints, promoting natural recovery. Studies indicate that over 2 million orthopedic implant surgeries occur yearly in the United States alone. These surgeries often leverage materials that mimic bone structure, ensuring better integration and support.
The mechanisms of action for these implants are varied. They may provide structural support, enable movement, or reduce pain by redistributing stress across the affected area. For instance, plates and screws hold fractured bones in alignment, allowing for proper healing. Over time, the body gradually replaces the implant with new bone tissue. However, this process can be hindered by factors such as age or underlying health conditions, leading to complications.
Data from the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons shows that approximately 15% of total joint replacement patients experience some form of post-operative complication. This highlights the need for ongoing research and development in implant technology. Despite high success rates, the journey to full recovery can still be inconsistent, and many patients require rehabilitation to regain optimum function. Balancing innovation with patient-centered care is essential in improving these outcomes.
Healing Process with Orthopedic Implants
Current Trends and Innovations in Orthopedic Implant Technology
Orthopedic implant technology has seen remarkable advancements in recent years. A report by the Global Industry Analysis predicts a growth rate of 6.1% in the orthopedic implant market from 2023 to 2030. This growth is driven by an aging population and a rise in sports-related injuries. New materials, such as bioactive ceramics and advanced polymers, are replacing traditional metals. These innovations enhance the durability and integration of implants into the body.
Current trends emphasize personalized medicine. Surgeons now use 3D printing to create custom implants tailored to the patient's anatomy. This approach has shown improved outcomes and quicker recovery times. However, challenges remain. Many implants still experience complications, such as infection or mechanical failure. An estimated 10% of patients report issues following surgery, indicating the need for ongoing improvements in design and materials.
Another key trend is the rise of minimally invasive techniques. These methods reduce recovery time and improve patient satisfaction. A recent study found that patients who undergo minimally invasive procedures have 30% less postoperative pain. Nevertheless, not all procedures can be adapted for minimal invasiveness, raising questions about the long-term efficacy of such approaches. Balancing innovation with patient safety continues to be a critical focus in the orthopedic field.
What is an Orthopedic Implant and How Does It Work? - Current Trends and Innovations in Orthopedic Implant Technology
| Type of Implant | Material | Application | Latest Innovations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hip Implant | Titanium Alloy | Hip Replacement Surgery | 3D Printing Technology |
| Knee Implant | Ceramic Composite | Knee Replacement Surgery | Biodegradable Materials |
| Spinal Implant | Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) | Spinal Fusion Surgery | Smart Implants with Sensors |
| Fracture Implant | Stainless Steel | Bone Fracture Repair | Enhanced Coating for Bone Integration |
Market Overview: Statistics on Global Orthopedic Implant Demand and Growth
The orthopedic implant market is rapidly growing. Recent data shows a significant rise in global demand. Increasing prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders drives this growth. Injuries and age-related issues lead to more surgeries. Hospitals and clinics seek innovative solutions for patients.
A variety of implants exist. These include screws, plates, and joint replacements. Each serves a specific purpose in healing bones and tissues. The technology behind these devices is advancing. More effective materials are being used. However, not all implants have long-term success. Complications can arise, and patient satisfaction varies.
Regional differences also impact the market. Developing countries show rising demand, while established markets are stable. Accessibility remains a concern. Some patients struggle with cost or availability. As we move forward, addressing these issues will be vital for growth. Better accessibility could enhance overall patient outcomes in the future.